The Structural Racism Effect Index (SREI) is composed of 9 domains:
Built Environment
Criminal Justice
Education
Employment
Housing
Income & Poverty
Social Cohesion
Transportation
Wealth
These domains were established through a thorough review of structural racism literature, identifying existing methods to quantify structural racism. The SREI collates variables across all of these existing domains to create scores for most census tracts in the country.
Domains and Variables
-
Building vacancy rate
Mobile homes
No internet access
Cancer risk
Low food access for SNAP recipients
-
Pretrial jail rate
Total jail rate
Law enforcement personnel per capita
-
No bachelor’s degree
Highest degree high school diploma
Per pupil spending
-
Unemployed
Low white collar occupations
Low retail job availability
-
Eviction rate
Foreclosure risk
Units without telephone
Units without plumbing
Crowding
Group quarters
-
Below federal poverty level
Below 200% poverty level
Public assistance
Family income
Per capita income
Supplemental poverty measure
-
Residential Segregation
Changed address in the past year
Single-parent household
Income gap
-
Transportation cost burden
Carpooled to work
No access to motor vehicle
Low public transportation
Low walking
Low biking
-
Aggregate home value
Median real estate taxes paid
Median home value
Median gross rent
Median monthly mortgage
Owner-occupied homes
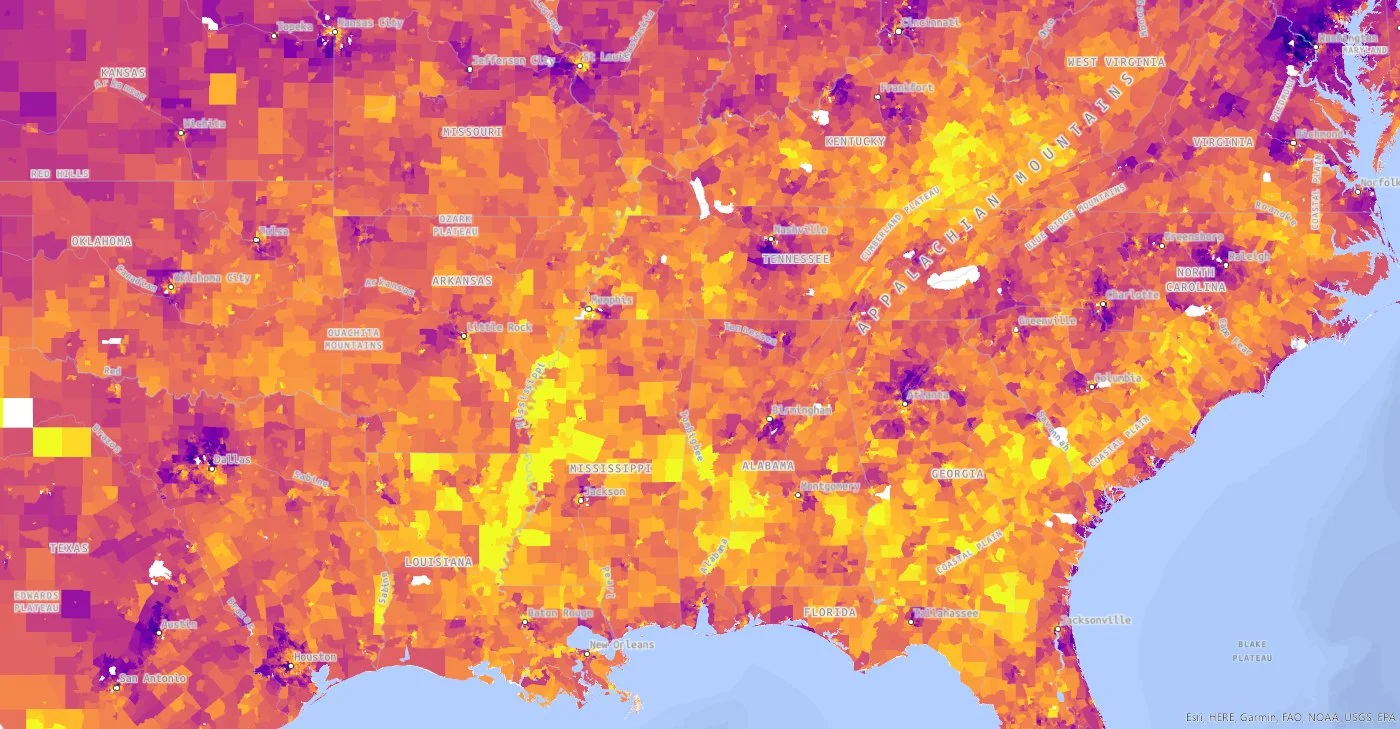
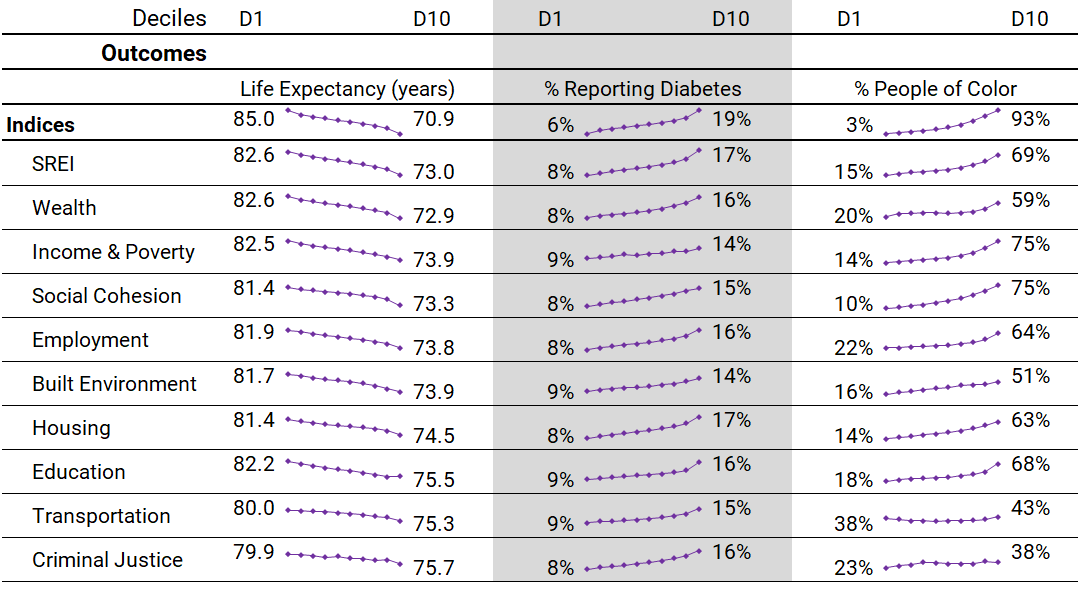
National Census-Tract-Level Distribution of Life Expectancy, Diabetes Prevalence, and Ethnoracial Composition: by SREI and Domain Scores
From the Appendix of the Health Affairs paper.
Each domain of the SREI is independently correlated with poor health outcomes and the the ethnoracial composition of a neighborhood. Unlike some area measures of the Social Determinants of Health, the SREI uses racism, not race, to explain inequities between neighborhoods. With the exception of ethnoracial segregation, the SREI does not use any measure of race or ethnicity in its composition.